what is aortic arch
 Aortic arch - Wikipedia
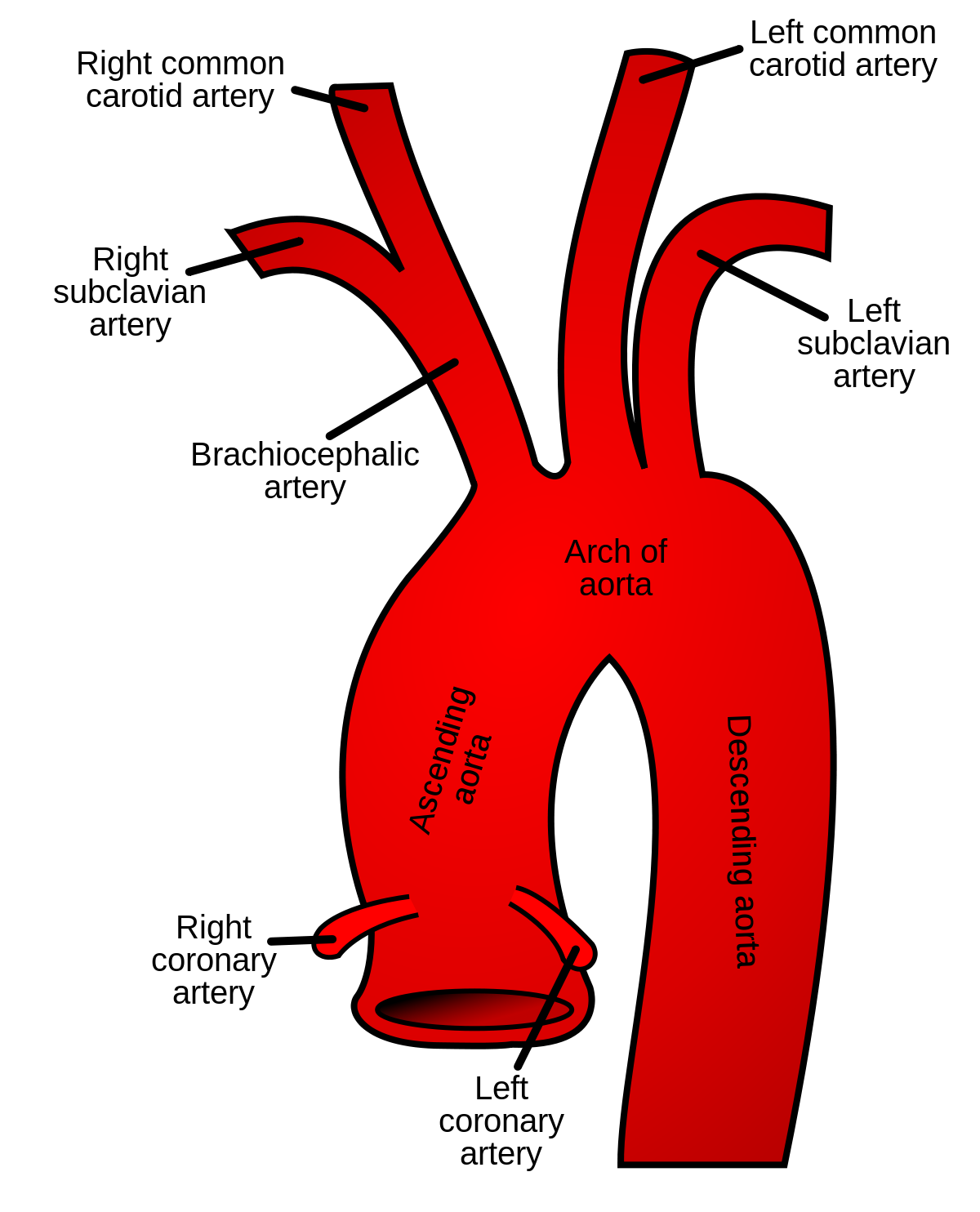
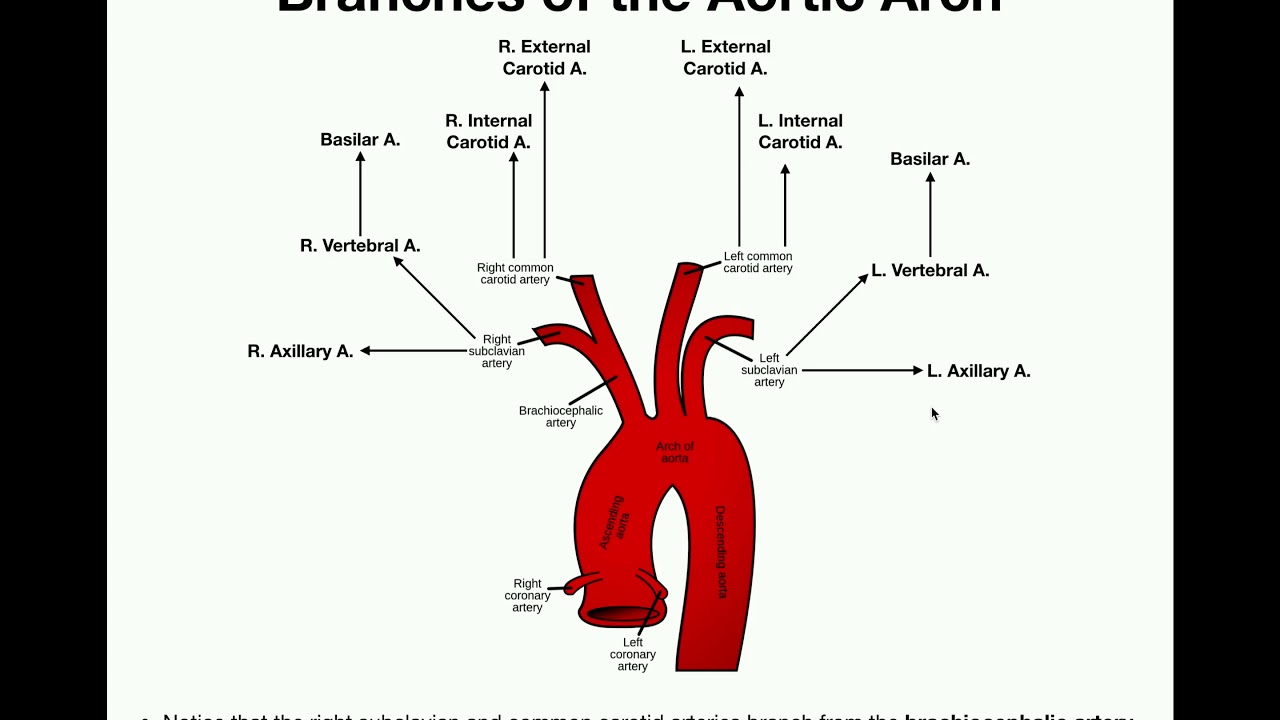
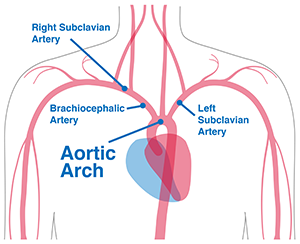
Aortic arch - WikipediaArctic ArcAortic arch The aortic arch has three branches, the , left , and left . The aortic bow and its branches shown. Details Continues as , Combination and vein cavaSupplies From its branches, the upper body, and . As part of the , the whole body, except the respiratory zone of the and the . The aortic arch, arc of the aorta, or a transversal aortic arch (English: ) is the part of the between the and . The arc travels backward, so that it finally goes to the left of the . aortic aortic aortic aortic arcContentsStructure[ ]In the cellular plane, the aorta and the aortic arch are composed of three layers: The , which surrounds the lumen and is composed of simple squamal epithelial cells; the , composed of smooth cell muscles and elastic fibers; and, the , composed of loose collagen fibers. Innervated by nervio terminals, the aortic arch is responsible for sensing changes in the dilation of the vascular walls, inducing changes in heart rate to compensate for changes in blood pressure. The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second right side, and runs at the beginning upward, backward, and left in front of the ; then travels backward on the left side of the and finally passes down on the left side of the body of the room. At this point the aortic bow continues as .:214 The aortic bow has three branches. The first, and greater, arch branch of the aorta is the , which is on the right and slightly before the other two branches and originates behind the manubrio of the sternon. Then the origins of the aortic arch to the left of the brachiophalic trunk, then ascend along the left side of the trachea and through the upper mediastinum. Finally, the exit of the aortic arch to the left of the common carotid artery of the left and ascends, with the common left carotid, through the upper mediastinum and along the left side of the trachea. An anatomical variation is that the left can emerge from the aortic arch instead of the left subclavian artery. The aorta arch forms two curvatures: one with its convexity upwards, the other with its convexity forward and left. Its upper border is usually about 2.5 cm below the border above the . Blood flows from the curvature above the upper regions of the body, located above the heart - that is, arms, neck and head. Out of the heart, the chest aorta has a maximum diameter of 40 mm in the root. By the time it becomes the ascending aorta, the diameter must be made 35–38 mm, and 30 mm in the arc. The diameter of the descending aorta should not exceed 25 mm. The arc of the Aorta is located inside the . Development[] The aortic arch is the connection between the ascending and descending aorta, and its central part is formed by the fourth left during early development. The connection to the lower part of the bow in fetal life. This allows the blood of the right ventricle to be drawn mostly to the lung vessels while developing. The final section of the aortic arch is known as the aorta isthmus. This is called because it is a close () of the aorta as a result of the decrease in blood flow when in fetal life. As the heart increases in size throughout life, the narrowing eventually spreads to become a normal size. If this does not happen, this can result in . The connection is connected to the final section of the bow in fetal life and when the ductus arterioso retreats. Variation[] There are three common variations in how the arteries branch from the aortic arch. In approximately 75% of individuals, the branching is "normal," as described above. In some individuals, the common left carotid artery originates from the brachiocephalic artery instead of the aortic arch. In others, the brachiocephalic artery and the common left carotid artery share an origin. This variant is found in approximately 20% of the population. In a third variant, the brachiocephalic artery is divided into three arteries: the common left carotid artery, the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery; this variant is found in an estimated 7% of individuals. Clinical Significance[]The aortic crab is the prominent shadow of the aortic arch on a front. is a surgical procedure in which the aortic bow is fixed to keep the open. Additional Images[] The aorta bow can be seen here, with the side to each side and emerging from the , below. A branch of the , the , passes under the aorta arch. The nerve looks here. References[ ]This article incorporates text in the 20th edition of (1918) abc15126abab8 External links[] Wikimedia Commons has media related to . ########################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################## Heart Sections Sections Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Other projects Languages

Aortic Arch Surgery - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

Interrupted Aortic Arch (IAA) (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth

Aortic arches - Wikipedia
Anatomy | Branches of the Aortic Arch - YouTube

Normal schematic diagram of the aortic arch and the great vessels... | Download Scientific Diagram
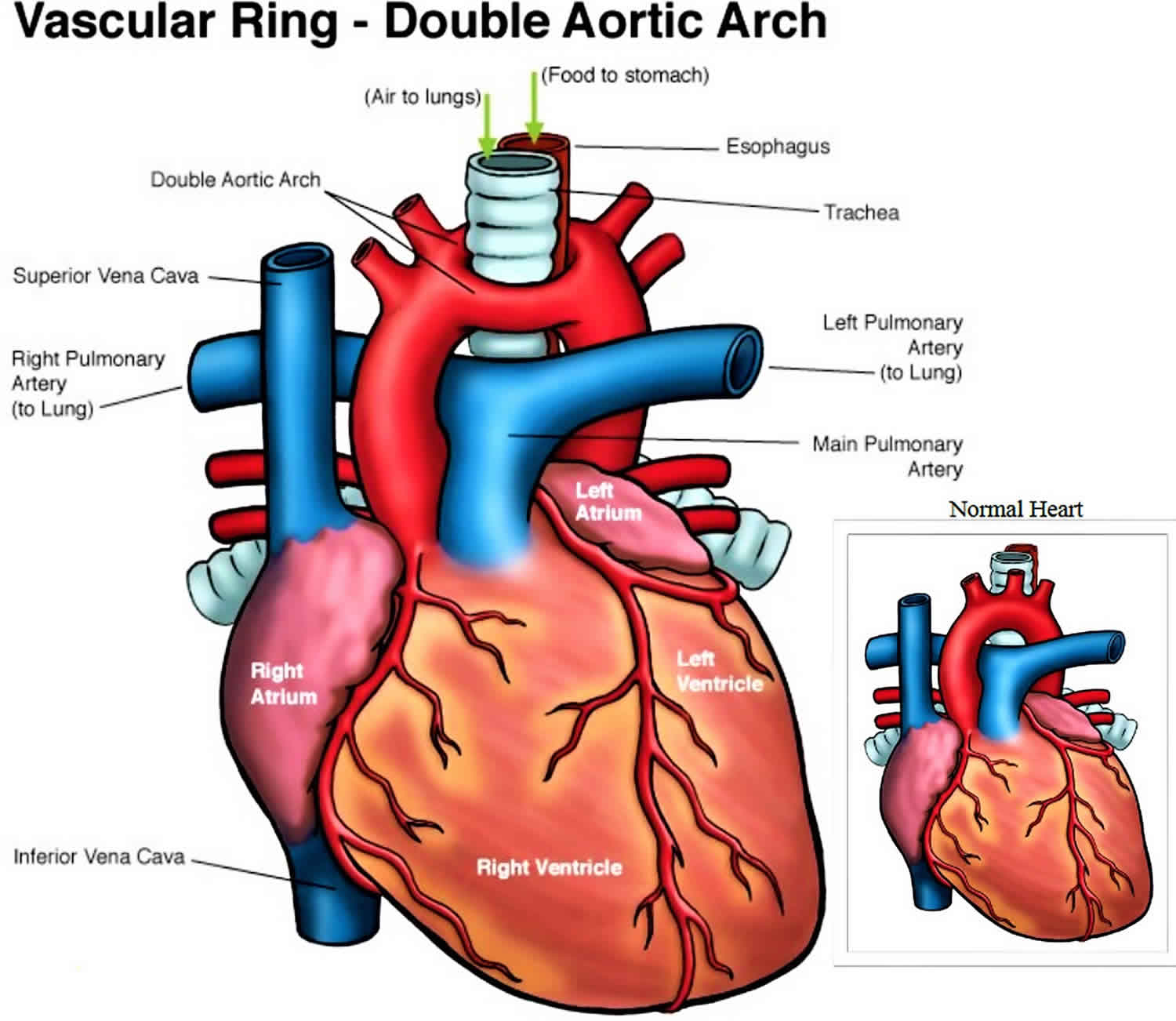
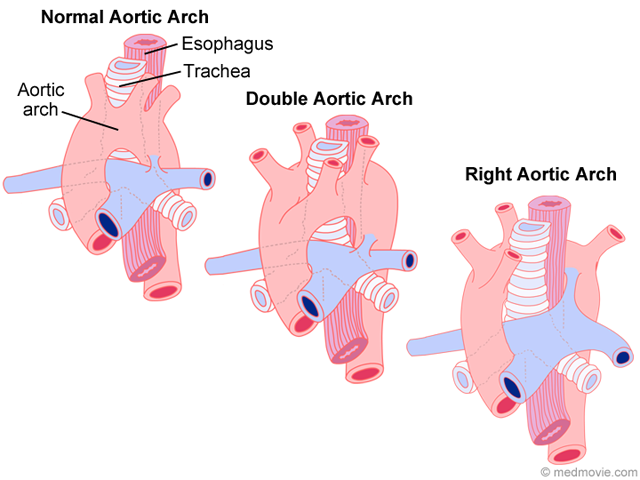
Double aortic arch causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
The RelayBranch Trial Introduces the First Minimally-Invasive Device for Total Aortic Arch Repair | Columbia University Department of Surgery
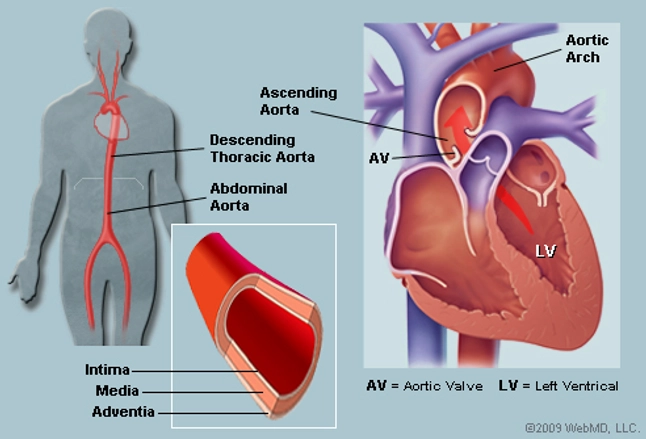
The Aorta (Human Anatomy): Picture, Function, Location, and Conditions

The derivatives of aortic arch arteries. Schematics showing the great... | Download Scientific Diagram

Congenital anomalies of the aortic arch - Priya - Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy
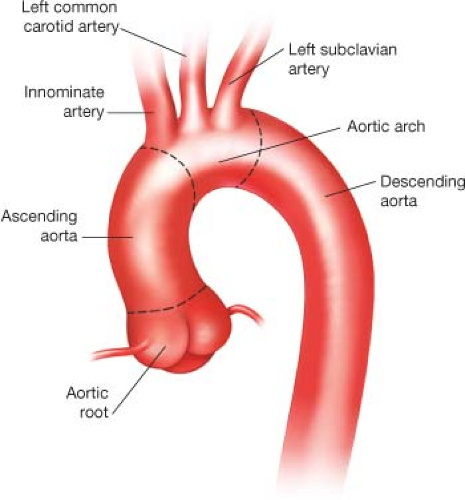
Aortic Arch/Great Vessel Surgery | Thoracic Key

Aortic arch - Wikipedia
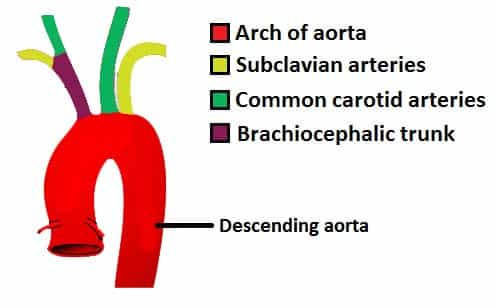
The Aorta - Branches - Aortic Arch - TeachMeAnatomy
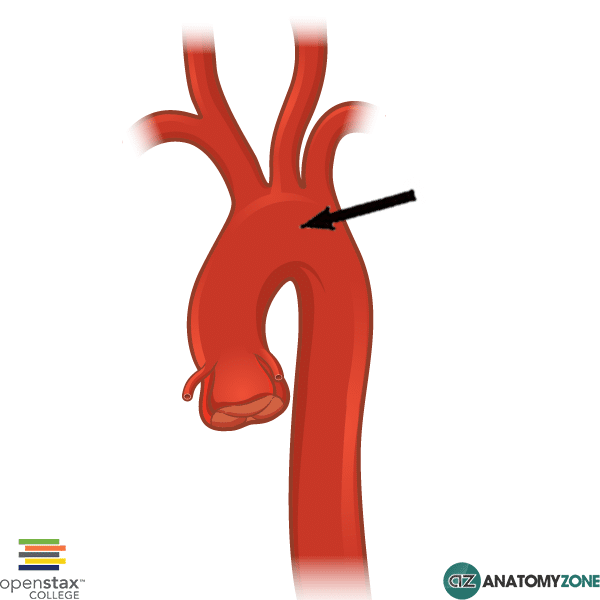
Aortic Arch - AnatomyZone
Variant anatomy of the aortic arch | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org

Pin by Laura Monk on Nursing | Anatomy and physiology, Medical knowledge, Medical coding

Interrupted Aortic Arch (IAA) (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
Aortic Arch Formation - Embryology Flashcards | Draw it to Know it
Bovine Aortic Arch Variant in Humans: Clarification of a Common Misnomer | American Journal of Neuroradiology

Aortic Arch: Anatomy, Branches, Function & Definition | Kenhub - YouTube
Aortic Arch - human anatomy organs

Double-Lumen Aortic Arch: Persistence of the Fifth Aortic Arch - The Annals of Thoracic Surgery

Frequency of variations in aortic arch anatomy depicted on multidetector CT - Clinical Radiology
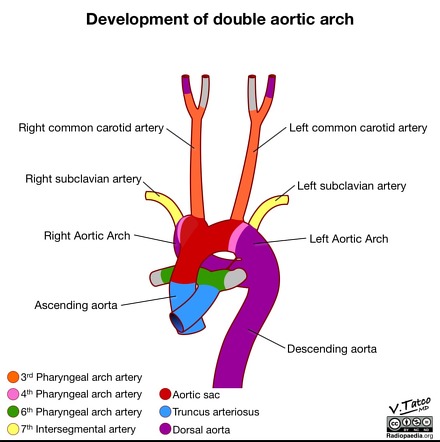
Aortic Arch Developmental Defects

Ascending Aortic Aneurysm: Repair, Surgery, and Size Criteria
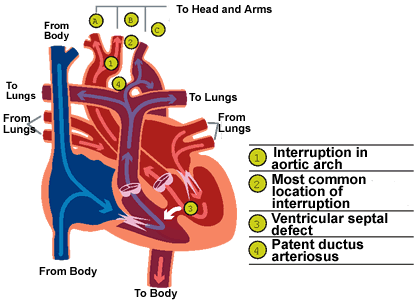
Interrupted Aortic Arch | CS Mott Children's Hospital | Michigan Medicine

Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms | Circulation
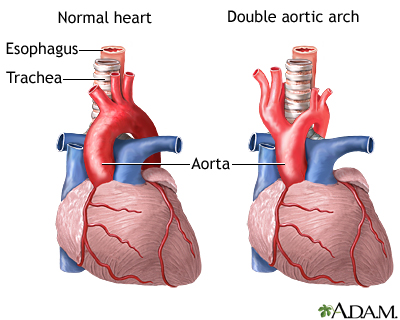
Double aortic arch: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
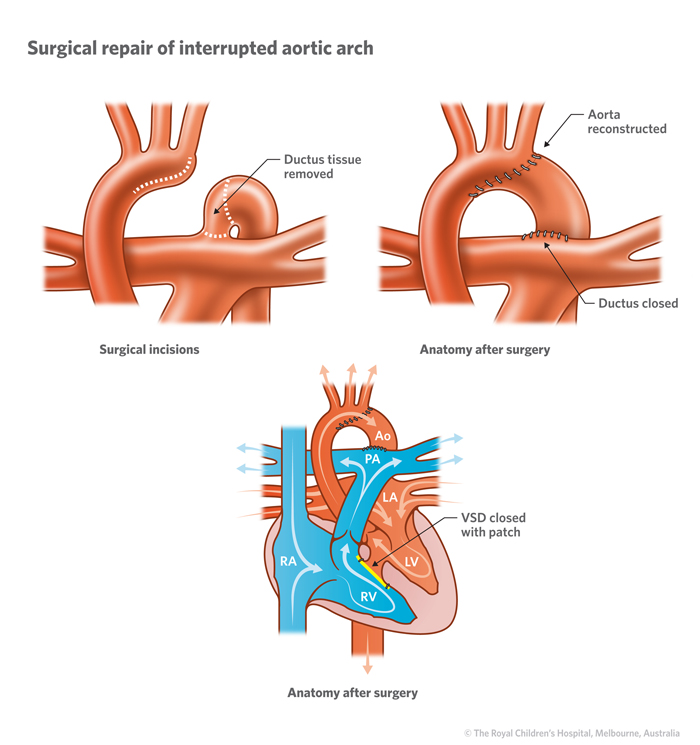
Cardiology : Interrupted Aortic Arch
Aorta - Wikipedia
Aortic Arch | neuroangio.org

Right Aortic Arch - Tiny Tickers

Endovascular exclusion of the entire aortic arch with branched stent-grafts after surgery for acute type A aortic dissection - ScienceDirect
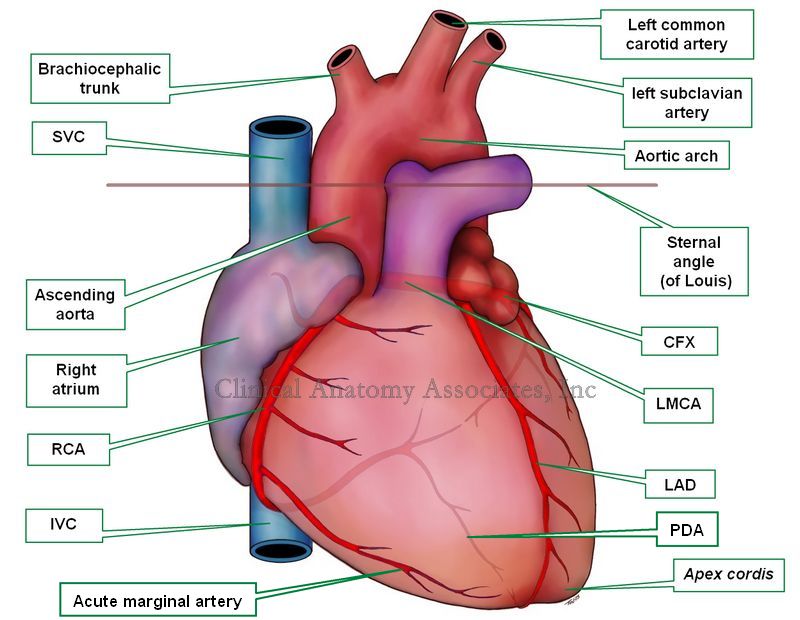
Aortic arch

Interrupted aortic arch variants - UpToDate

Aortic Arches Explained - YouTube

Surgical treatment of an aneurysm in the right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery - The Annals of Thoracic Surgery

Atypical aortic arch branching variants: A novel marker for thoracic aortic disease - The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
Congenital Defects Tutorial - Congenital Heart Defects | Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy

Celoria-Patton classification of interrupted aortic arch (illustration) | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
Posting Komentar untuk "what is aortic arch"